Anatomy of the eye
The eyes are one of the most important sensory organs that are available to man, because about 70% of the information about the outside world perceives people through the visual analyzer. Organ of vision or visual analyzer - is not only eye. Actually it's the eye of the peripheral organ of vision.
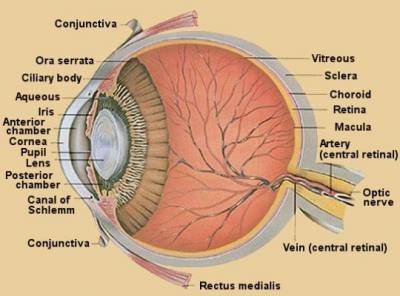
Information obtained by the apparatus of the eyeball, is transmitted by the optic pathways (optic nerve, optic chiasma, optic tract), first in the subcortical centers of vision (lateral geniculate body), followed by visual and visual radiance beam Grazioli in higher visual center in the occipital lobes the brain.
The peripheral part of the vision are:
- eyeball
- security apparatus of the eyeball (the upper and lower eyelids, eye socket)
- accessory apparatus of the eye (lacrimal gland and its ducts, as well as the oculomotor apparatus, consisting of the muscles).
The eyeball is the main place in the orbit or eye socket, which is the seat of the bone and the eye is also used to protect it. Between the orbit and the eyeball is the fatty tissue that performs a damping function and there are blood vessels, nerves and muscles. Eyeball weighs about 7 grams. The shape of the eyeball is slightly flattened in the anteroposterior direction the ball.
The wall of the eyeball consists of three layers:
The outer shell. Most of it is a protein dense opaque fabric. This is the sclera or white of the eye. Front sclera becomes a smaller part of the outer membrane - the transparent cornea. Place of transition of the sclera into the cornea called the limbus. The cornea is the front of the eyes, through her eyeball penetrating rays of light. Ellipsoidal shape of the cornea, the diameter of the vertical - 11mm, horizontal - 12 mm. The thickness of the cornea and sclera approximately 1 mm. Both of these membranes are very dense and strong, which helps maintain the shape of the eye and intraocular pressure. Transparency of the cornea due to its unique structure, it all cells are in strict order of the optical. The cornea is not only missing, but also refracts light rays.
Tunica media of the eyeball - vascular. The choroid consists of:
- actual vascular membrane (Choroid) in the back of the eye
- ciliary or ciliary body in the middle section
- anterior - iris.
Iris or iris in the anterior part of the eye. It consists of loose connective tissue and vascular network. In the center of the iris is opening - the pupil, who plays the diaphragm, regulating the amount of light reaching the eye. Changing the diameter of the pupil under the influence of light emission is called the reaction of pupils to light or pupillary reflex. Narrows and widens the pupil through the work of two muscles located in the iris. This muscle is a muscle and constrict the pupil expands the pupil. The color of the iris of the number of its special cells melanophores containing melanin. The more melanin, the darker the color of the iris. For peripheral edge of the iris or ciliary changes in ciliary body. Ciliary body from the outside covered with sclera. It has a ring-shaped and consists of connective tissue, blood vessels, ciliary muscle and ciliary processes of the body. By the spikes of ciliary body with a special round ligament attached lens. One of the most important functions of the ciliary body is involved in the process of accommodation. With the reduction of the ciliary body and lens is weakened ligament assumes a more convex shape, with improved vision near objects and vice versa, ciliary muscle relaxes, the lens takes more than a flat shape, to improve distance vision. Another function of the ciliary body is the production of intraocular fluid, through which feed on education eyes that do not have their own vessels (cornea, lens, vitreous body) and provides a constant intraocular pressure. Choroid consists of a large number of vessels and took back two thirds of the choroid. Its main function - power of the retina.
The inner shell of the eyeball - retina. It is part of the nervous system and is the first department of the visual analyzer. In the retina, the light energy is converted into nerve impulses and is the primary analysis of visual information. The upper layer of the retina - the pigment. It absorbs the light, reducing its diffusion inside the eye, and it also produced visual material. The next layer contains the processes of the retina - rods and cones. Spines contain visual substance (visual purple) - rhodopsin (rods) and iodopsin (cones). The rods and cones send jitters farther than bipolar cells, and these in turn ganglion cells. Spines of these cells are collected in the optic nerve. Optically active part of the retina can be seen when examining the eye. It is called the fundus. In the fundus may be considered vessels, optic disc, as well as a yellow spot. The yellow spot - an area of the retina, where concentrated the maximum number of cones, are responsible for color vision.
The interior of the eyeball is:
- intraocular fluid
- crystalline lens
- vitreous.
Intraocular fluid located in front of the eye. The space between the cornea and the iris is called the anterior chamber between the iris and lens - the back of the camera eye. Fluid inside the chambers are constantly circulating.
The lens is a transparent body, takes the form of lentils or lenticular lens. With the circular (tsinnovoy) ligament he is suspended from the ciliary body spikes. The lens is involved in the breaking of light rays and in the act of accommodation. For the lens is the vitreous body. It occupies most of the cavity of the eyeball. It is a clear studneobraznaya mass containing 98% water.
Vitreous involved in the breaking of light rays, and also supports the tone and shape of the eyeball.
By eye protective devices include:
ever
eye socket.
Eye socket or orbit - a bony receptacle of the eyeball, its ligaments and suspensory apparatus of the eye muscles, fat. Wall of the orbit formed by the cranial and facial bones.
The upper and lower eyelids protect the eyeball from falling into various subjects. They are closed even when driving and air at the slightest touch to the cornea. With the blinking motion vector from the surface of the eyeball removed fine dust particles and evenly distributed lacrimal fluid. Free edges of the eyelids are tight to each other when they are closing. The skin is thin century, it is easy to gather. Subcutaneous tissue contains very little fat. Under the skin are muscles of age:
- circular muscle of the eye, through which the eyelids are closed
- muscle lifting the upper eyelid.
The inner surface is covered with a mucous membrane century - the conjunctiva. The conjunctiva has many nerve endings, and its cells secrete a special secret, lubricating the surface of the eyeball.
By adnexa eye include:
- lacrimal apparatus
- muscular system.
Lacrimal apparatus consists of the lacrimal gland, located in verhnenaruzhnoy orbital wall, tear ducts, lacrimal sac and tearfully-nasal canal. Lacrimal gland constantly produces tears. Lacrimation increased during stimulation of the cornea and in tears. Tear collected from the inner corner of eyes, and then displayed on the nasolacrimal canal into the nasal cavity.
Muscular system - in the orbit are eight muscles involved in movement of the eyeball. With these muscles rotate the eyeball can in all directions.
With this material are reading...
My Great Web page
Attachments: |

