Anatomy of a duodenum
Duodenum - is part of the intestine, which adjoins directly to the stomach and starts from the sphincter that regulates the flow of bolus from the stomach into the duodenum. The average length of the duodenum in the adult form of about 30 cm of the duodenum resembles a horseshoe.
There are four parts:
The upper part of the duodenum is called the bulb. It directly connects to the stomach. Then comes the descending part, which is directed vertically downwards. On the down side is the wall of the papilla Vater. Through the papilla Vater into the duodenum runs a common duct, which is formed from a joined ducts: common bile and pancreatic (pancreatic duct). In this part there is also a small papilla, which separates the additional pancreatic duct. 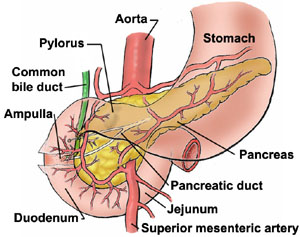
The horizontal portion of the duodenum from the bottom is covered with peritoneum. It is adjacent to the lower vena Vienna, aorta and pancreas. Further changes in the horizontal part of the rising, which passes into the small intestine. Neuro-muscular system provides a peristaltic duodenal ulcer reduce the pendulum, which promote food bolus toward the intestines.
The inner surface is covered with duodenal mucosa. The surface of the mucosal epithelium is made. The cells of the epithelium of the villi form. Between the fibers are so-called intestinal crypts, which come off the outlets of glands of the duodenum. These glands produce a thick viscous secretion that is alkaline.
In the duodenal mucosa is a huge number of glands that produce secretin, cholecystokinin, and other kinazinogen All substances that are synthesized in the duodenum are involved in digestion, regulation of motility of the gastrointestinal tract, biliary tract and participate in some of the other processes in body. A very important function of the glandular cells of the duodenum is the formation of the protective mucus barrier. Requires continuous synthesis of mucus, which is produced blennogenic cells.
With this material are reading...
My Great Web page
Attachments: |

